If you get to troubleshoot some unknown Linux server, running these few commands will be useful.
1. Check who's logged in
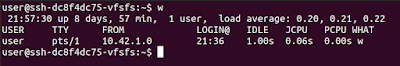
w
This is a cool one-letter command to see who else logged into the server. It will list the usernames and even you can find the IP and the connection type. In the following example, I've logged in as the "user".
2. Identify the OS
There are different commands to identify what kind of Linux distribution that you are dealing with. Knowing this is crucial to decide what commands to use later.
cat /etc/os-release
Usually, in Linux distributions, you have a file /etc/os-release. Basically, you can see everything you need to know about the OS in this file.
3. See running processes
top
This basically lists the processes running with the CPU and memory consumption.
With this, we can get an idea about what kind of apps running on the server and if any of them uses too much CPU or memory.
4. See disk space usage
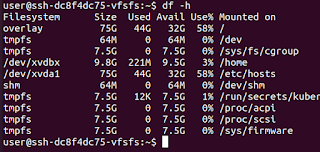
df -h
This provides the disks that are being used and their usage of them. If there's a disk with 100% or running out of space, you can identify that.
5. See memory usage
free -h
With this, you can see the memory usage of the system. If the system is running out of memory, you can spot that.
6. See the command history
This is one of the critical commands that you can use to identify what commands have been used in the past. This has saved my neck on several critical occasions so I'm forever grateful to the person who developed the history command lol.
It lists the history of commands that has been executed in the past. If you don't know anything about the server, this is so much important to see what services have been used in the past, and which commands have been executed.
Also, if you need to find out about a specific service you can grep the history to identify the commands related to that service.
eg:
history | grep nginx
7. See network ports
netstat -ntlp
This command allows you to see which ports are open and listening in the system. Based on that, you can even say if an application server (something like Apache, Nginx, or even Tomcat) is running or not.
Running these commands will give you a basic idea about the system that you are about to deal with.
If there are any other commands that you think will be important to deal with an unknown system, please comment below :)





Comments
Post a Comment