There are two main commands in Ubuntu for creating users. I've found them confusing and I always forget which to use when. So, thought to write them down clearly as a quick reference.
TLDR;
adduser - Interactive tool, creates home directory and prompts for password and more details.
useradd - A low level tool to creat a user. Doesn't create home dir if not specified. Use passwd command to add/change password for the user.
Easier Command
adduser
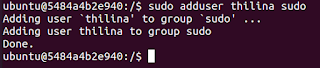
If you want to create a typical user for Ubuntu, just use "adduser" command. This is an interactive high level tool which will take in username, and more details including password. It will create the home directories as well.
adduser <username>
adduser <username> <group name>
Not so easier commands
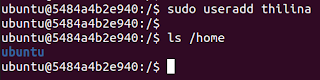
This ia low level tool which would create the user. Home directory is not created unless specified.
useradd <username>
useradd with home directory
useradd -m <username>
Add user to a group
In oder to add user to a group, you can also use usermod command.
sudo usermod -aG <group name> <username>
Also this can be use for various user modifications like changing the home directory etc. Refer the man pages for more details.
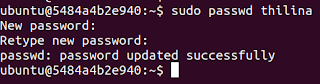
passwd
This can be used to set a password or change a password to a user.
passwd <username>
Delete a user
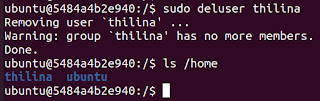
You can use deluser command to delete a user.
deluser <username>
Notice that home directory still exists even after deleting the user.
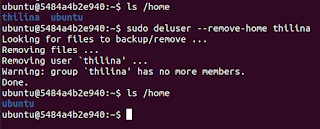
If it requires to delete the home directory, you can use --remove-home flag.
deluser --remove-home <username>
All in all, adduser command is a highlevel interactive tool which can do same thing as using combinations of multiple low level commands. Even though useradd command is a low level tool, this is much useful if you need to create system users with various requirements. You can even set an expiration for a user with this command. Check out the command man page for more details.


Comments
Post a Comment